- Bonder & Flip Chip
- Atmospheric Plasma Cleaner
- Vacuum Plasma Cleaner
- Spin Rinse Dryer
- Dispensing & Micro/Nano Printing System
- Lithography Process Systems
- Diffusion and LPCVD Furnaces
- Rapid Thermal Processing & Annealing
- Vacuum Soldering Systems
- Parylene Coating System
- Deposition System
- Hollow Cathode Plasma Source
- Plasma Etching System
- Sintering Presses
- Wet Process & Plating Tool
- Vacuum Chamber
- Electron Beam & Photo Resist
- Deposition Materials
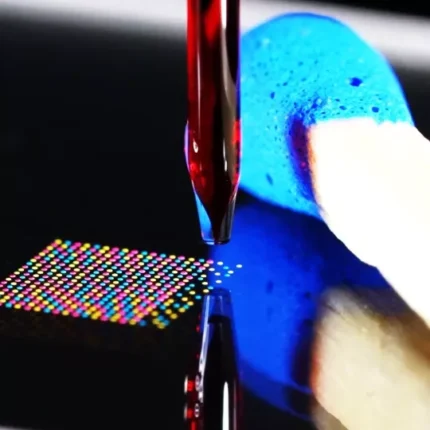
Non-contact – Nano to Microliter Dispenser
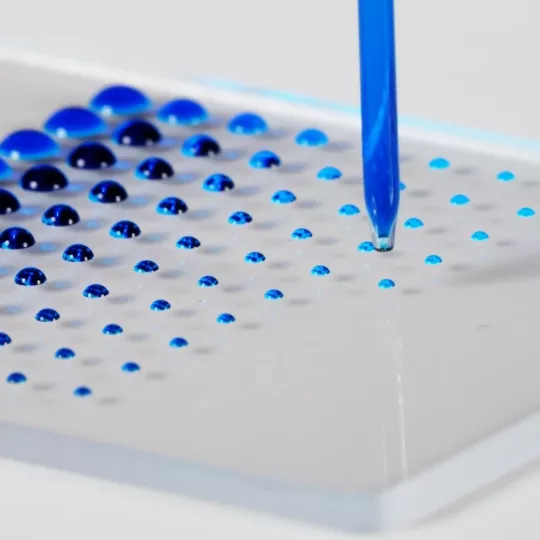
The M2–MicroDispenser (M2MD) is a cutting-edge nanoliter dispenser that utilizes variably fast volume displacement as a dispensing technique. With a minimum dispense volume of 10 nanoliters and the capability to increase it to 5 microliters, this nanoliter dispensing technology offers flexibility in handling a wide range of volumes.
The M2MD also offers a bulk-dispenser version, in which a glass vial attached to the dispenser is filled with the solution to be dispensed. This bulk-dispenser configuration simplifies the dispensing process and ensures a continuous supply of the solution.
Nanoliter dispensers, like the M2-MicroDispenser, offer precise and accurate dispensing of small liquid volumes, making them invaluable tools in scientific research fields as well as production environments. The advancements in non-contact dispensing technology, along with the ability to customize the dispenser to meet specific requirements, further enhance their versatility. By incorporating nanoliter handlers into laboratory workflows, researchers can achieve improved results and streamline their liquid-handling processes.
The M2MD can operate on all of the M2-family Microdispensing Instruments.
Category: Dispenser Types
Description
Key Features
- Single-droplet volume 10 nL to 5 µL
- Up to 50 Hz dispensing frequency
- Volume accuracy cv 2 % to 5 %
- Bulk dispensing or Aspirate/Dispense types
- Glass capillary or disposable, plastic tip
- Quick change of capillary switch to tip
Functional Principle
The functional principle of nanoliter liquid dispensers revolves around an ultra-fast solenoid valve and two independent parameters: pressure and valve-opening time. These parameters determine the dispense volume. For small volumes (< 50 nanoliters), fast volume displacement is used for dispensing, while larger volumes are dispensed by overlaying a pressure-driven flow.
To compensate for the dispensing of more viscous liquids, the valve opening time can be reduced by raising the pressure. Additionally, if splashing occurs on the target surface, the liquid impact velocity can be reduced to prevent any unwanted effects.
Dispensing Modes
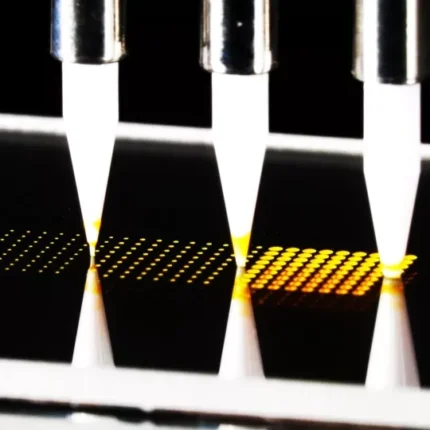
- Stop-to-spot with Z-moves: The dispenser stops for each droplet deposition and moves up and down between consecutive positions to bypass possible obstacles. These movements cost time but can be necessary when dispensing onto specific locations of a non-planar, 3-dimensional target.
- Stop-to-spot, no Z-moves: Without the need to move the head up between consecutive positions, dispensing is much faster. This is always the case when dispensing onto planar targets.
- On-the-fly: The dispenser “flies” over the target and releases a droplet on defined positions during the flight. That way, up to 50 droplets per second can be deposited, each at its own specific coordinates.
Single-Droplet Volume Range
The M2-MicroDispenser covers the entire range of single-droplet volumes, ranging from 10 nanoliters to 5 microliters. Instead of dispensing multiple smaller droplets for nanoliter volumes, the dispenser can deliver a larger droplet. The advantages of dispensing a larger droplet include reduced risk of splashing (satellite drops) and increased dispensing speed. It is recommended to operate the dispenser at a maximum frequency of 20 Hz, although higher frequencies may be achievable depending on the properties of the liquid being dispensed.
Two Kinds of Dispensing Tip
Our nano dispenser offers two types of dispensing tip, allowing users to choose the most suitable option for their specific application. The first option is a thin glass capillary with a tapered end, while the second option is a conically shaped, disposable, plastic tip. The choice between these two tips depends on factors such as the nature of the liquid and the desired dispensing precision.